| .. | ||
| reward | ||
| __init__.py | ||
| comm.py | ||
| consumer.py | ||
| grpo_consumer.py | ||
| inference_backend.py | ||
| launch.py | ||
| loss.py | ||
| producer.py | ||
| profiling_utils.py | ||
| README.md | ||
| utils.py | ||
Distributed RL Framework for Language Model Fine-Tuning
This repository implements a distributed Reinforcement Learning (RL) training framework designed to fine-tune large language models using algorithms such as GRPO and DAPO. It supports multi-node and multi-GPU setups, scalable rollout generation, and policy optimization using libraries like VLLM. Currently, we support two Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Reward (RLVR) tasks: solving math problems and code generation.
Please note that we are still under intensive development, stay tuned.
🚀 Features
- Distributed Training with Ray: Scalable to multiple machines and GPUs.
- Support for GRPO and DAPO: Choose your preferred policy optimization algorithm.
- Model Backends: Support
vllmas inference backends. - Rollout and Policy Decoupling: Efficient generation and consumption of data through parallel inferencer-trainer architecture.
- Evaluation Integration: Easily plug in task-specific eval datasets.
- Checkpoints and Logging: Configurable intervals and directories.
🛠 Installation
Prepare Develop Environment
Install Colossalai & ColossalChat
git clone https://github.com/hpcaitech/ColossalAI.git
git checkout grpo-latest
BUILD_EXT=1 pip install -e .
cd ./applications/ColossalChat
pip install -e .
Install vllm
pip install vllm==0.7.3
Install Ray.
pip install ray
Install Other Dependencies
pip install cupy-cuda12x
python -m cupyx.tools.install_library --cuda 12.x --library nccl
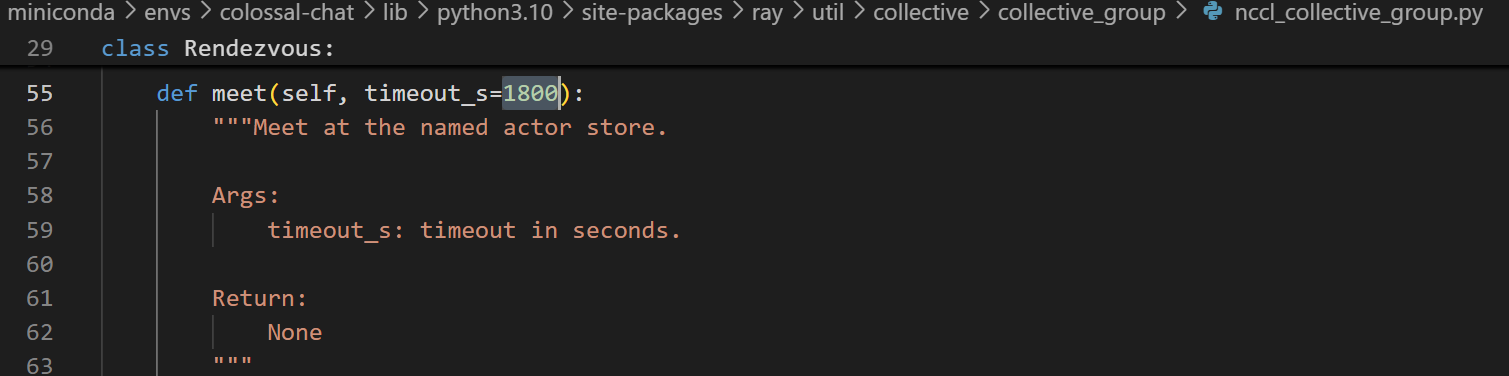
To support long input/output sequence length (e.g., 32K), you may need to manually change the default setting (180 seconds) for the timeout_s variable in your ray installation to a larger value as shown in the screenshot below.
Prepare Model & dataset
huggingface-cli download --local-dir-use-symlinks False Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B --local-dir /models/Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B
Architecture Design
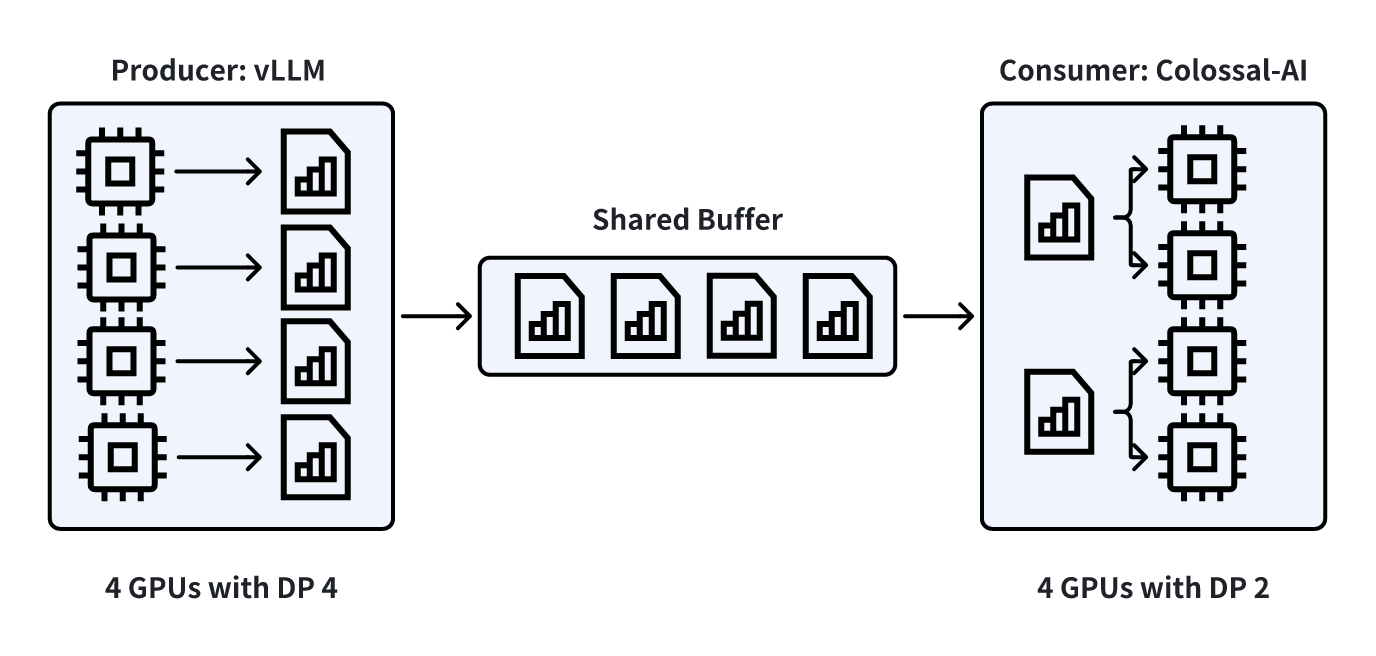
- Producer: inference engine which rollouts out examples and saves them into a shared buffer.
- Consumer: training framework which takes training examples from the shared buffer and train the policy model.
Key features for Producer-Consumer Pattern:
- Buffer: Acts as a shared queue where the producer adds data and the consumer removes data.
- Concurrency: Rollout and training can work concurrently.
🧠 Data Format
Samples in the training or evaluation .jsonl file should follow the format specific to the type of task. We currently support two RLVR tasks: solving math problems and code generation.
Math Data Format
{
"messages": {
"role": "user",
"content": "Simplify $\\sqrt[3]{1+8} \\cdot \\sqrt[3]{1+\\sqrt[3]{8}}$."
},
"gt_answer": "3"
}
Code Data Format
We support Prime code dataset format. Inputs and outputs in test cases should be two lists containing only strings and matching in the number of elements. Your prompt must properly instruct the LLM to generate code to read test cases from stdin and output results to stdout.
{
"messages": {
"role": "user",
"content": "Solve the following coding problem using the programming language python:\n\nMikhail walks on a Cartesian plane. He starts at the point $(0, 0)$, and in one move he can go to any of eight adjacent points. For example, ..."
},
"test_cases": {
"inputs": [
"3\n2 2 3\n4 3 7\n10 1 9\n"
],
"outputs": [
"1\n6\n-1\n"
]
}
}
⚙️ Hyperparameters & Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
--model |
Model path or identifier | /path/to/model |
--dataset |
Path to training .jsonl |
/path/to/train_data.jsonl |
--eval-dataset |
JSON of task:eval_dataset_path pairs | {"eval_1":"/path/to/eval_1.jsonl"} |
--project |
Project name | Project1 |
--num-episodes |
Number of training episodes | 1 |
Distributed Training
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
--num-trainers |
Number of trainer processes | 4 |
--num-inferencer |
Number of inferencer processes | 4 |
--inference-batch-size |
Prompts per inference step | 8 |
--inference-microbatch-size |
Per-GPU batch size for inference | 8 |
--train-batch-size |
Prompts per trainer step per dp group | 8 |
--train-minibatch-size |
Mini-batch size before forward pass | 8 |
--train-microbatch-size |
Per-GPU batch size for training | 2 |
Sampling
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
--backend |
Generation backend, choose from vllm |
vllm |
--temperature |
Sampling temperature for generation | 1.0 |
--top-k |
Top-K sampling parameter for generation | None |
--top-p |
Top-P sampling parameter for generation | 1.0 |
--system-prompt |
System prompt, optional, default to the default system prompt for each reward types. For more information, refer to the reward type section | Please reason step by step, and put your final answer within \\boxed{}. |
--max-new-tokens |
Max generation tokens | 3584 |
--max-prompt-tokens |
Max prompt tokens | 512 |
GRPO Specific
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
--algo |
Algorithm (GRPO or DAPO), for more customization refer to GRPO Settings |
GRPO |
--learning-rate |
Learning rate | 1e-6 |
--kl-coeff |
KL penalty coefficient, if nonzero, a reference model will be used | 0.01 |
--reward-type |
Reward signal type (choose from 'think_answer_tags', 'boxed', 'code') For more information, refer to the reward type section | think_answer_tags |
--eval-interval |
Evaluation interval in number of training steps (positive value to enable evaluation) | 10 |
Logging and Checkpointing
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
--save-interval |
Training steps between checkpoints | 20 |
--save-dir |
Checkpoint directory | ./model |
--eval-save-dir |
Evaluation save path | ./eval |
--rollout-save-dir |
Rollout logs directory | ./rollouts |
Miscellaneous
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
--ray_dir |
Custom Ray temp dir of a running Ray cluster (optional) | None |
--master_address |
Master address of a running Ray cluster | None |
--master_port |
Master port for torch DDP | 29506 |
⚙️ GRPO Settings
In addition to the two default training settings provided—GRPO and DAPO—users can customize their training by changing the following hyperparameters in grpo_config in rl_example.py.
| Argument Name | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
filter_range |
Filters out rollout group if the success rate within that group is out of this range. | [0.01, 0.99] |
dynamic_batching |
Enables dynamic batching as described in the DAPO paper. | True |
clip_eps_low |
epsilon_low in DAPO in equation in DAPO paper | 0.2 |
clip_eps_high |
epsilon_high in DAPO equation in DAPO paper | 0.28 |
skip_threshold |
If ratio is above this threshold, the sample is skipped to avoid instability. | 20.0 |
loss_variation |
Type of loss variation. Supports "token_level" for token-wise policy gradient loss and sample_level for original GRPO loss. |
"token_level" |
soft_over_length_punishment |
Whether to use soft overlength penalty in DAPO paper or not. | True |
cache_length |
L_cache parameter for soft overlength penalty in e.q. 13 in DAPO paper |
min(1024, int(args.max_new_tokens / 4)) |
filter_truncated_response |
Mask out truncated responses in loss calculation. | True |
🔄 Constraints and Notes
-
num_inferencer + num_trainer == NUM_GPUs -
num_inferencer % num_trainer == 0 -
(num_inferencer * inference_batch_size) % (num_trainer * train_batch_size) == 0 -
train_batch_size >= train_minibatch_size >= train_microbatch_size -
inference_batch_size >= inference_microbatch_size -
Set microbatch sizes based on VRAM capacity
-
To use tensor parallelism on inferencer
- set backend to
vllm - change
tensor_parallel_sizeininference_model_configin rl_example.py - set
num_inferencer = NUM_INFERENCE_GPUs / tensor_parallel_size
- set backend to
-
To set tensor parallelism / pipeline parallelism / zero stage
- change corresponding settings in
plugin_configin rl_example.py
- change corresponding settings in
-
Ensure rollout generation rate matches trainer consumption:
num_inferencer * inference_batch_size % ( num_trainer * train_batch_size / train_pipeline_parallelism_size / train_tensor_parallelism_size ) == 0 -
Model weights sync every:
(num_inferencer * inference_batch_size) / (num_trainer * train_batch_size / train_pipeline_parallelism_size / train_tensor_parallelism_size) -
Reward Type
We currently support three reward types---
think_answer_tags,boxed,code, each varies in details such as how answer is extracted and the reward calculation process. Please select one fromthink_answer_tags,boxedfor math problem solving and usecodefor code generation. The default system prompt for each reward type is as follows. Please make sure your system prompt provides information for the answer to be correctly extracted from model responses.-
think_answer_tags
Answer extraction: extract the content between the last
<answer>,</answer>tags.You are a helpful assistant. The assistant first thinks about the reasoning process in the mind and then provides the user with the answer. The reasoning process and answer are enclosed within <think> </think> and<answer> </answer> tags, respectively, i.e., <think> reasoning process here </think><answer> answer here </answer>. Now the user asks you to solve a math problem that involves reasoning. After thinking, when you finally reach a conclusion, clearly output the final answer without explanation within the <answer> </answer> tags, i.e., <answer> 123 </answer>.\n\n -
boxed
Answer extraction: extract the last content marked by
\\boxed{}Please reason step by step, and put your final answer within \\boxed{}. -
code
Answer extraction: extract code inside
```python\n...```You are a helpful assistant.
-
🧪 Example: single machine 8-GPU Zero2 Strategy
python rl_example.py \
--dataset /path/to/train_data.jsonl \
--model /path/to/Qwen2.5-3B/ \
-t 4 -i 4 \
-b vllm \
-ibs 2 -tbs 4 -tMbs 1 -tmbs 4 -imbs 1 \
-rt boxed \
-g 4 \
-ibs 1 \
-tbs 2 \
-tMbs 1 \
-tmbs 2 \
-imbs 1 \
-s "Please reason step by step, and put your final answer within \\boxed{}." \
-tMbs 8 \
-p GRPO-Train-Align-Debug \
🧪 Example: multi-machine TP+PP Strategy
Create ray cluster on multi-machine
For example, now we have 4 nodes and their IPs are 10.0.0.3, 10.0.0.4, 10.0.0.5, 10.0.0.6. We use 10.0.0.3 as master node. First we start a ray cluster on 10.0.0.3:
ray start --head --node-ip-address=10.0.0.3
Then, for each slave node (10.0.0.4/10.0.0.5/10.0.0.6), we add to the ray cluster by following code:
ray start --address='10.0.0.3:6379'
Modify plugin_config in ./applications/ColossalChat/rl_example.py
plugin_config={
"tp_size": 4,
"pp_size": 2,
"microbatch_size": max(
1, args.train_microbatch_size // 2
), # microbatch size should be set to train_microbatch_size // pp_size
"zero_stage": 1,
"max_norm": 1.0,
}, # for pp, tp
# Hint1: replace /models/Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B to your model path
# replace /datasets/train-alignment.jsonl to your dataset path
python rl_example.py
-m /path/to/Qwen2.5-Math-7B/ \
-d /path/to/train_data.jsonl \
--master_address '10.0.0.3'
-t 16 \
-i 16 \
-p GRPO-Train-Align-Debug \
-g 2 \
-ibs 1 \
-tbs 2 \
-tMbs 1 \
-tmbs 2 \
-imbs 1 \
-b vllm \
-e 2 \
-rt boxed \
-s "Please reason step by step, and put your final answer within \\boxed{}."
Acknowledgement
Colossal-RL is a distributed version of ColossalChat and inspired by a few awesome open-source projects. We would like to express our gratitude to the following awesome open-source projects and algorithms: GRPO, DAPO, TRL, Verl, OpenRLHF, StreamRL, Qwen, Logic-RL.